Cybersecurity in Healthcare sector: X-rays and how to protect yourself
Cybersecurity in the healthcare sector is one of the most important battlefronts in the current digital landscape.
Recent improvements in communication and computing technologies have greatly increased the efficiency of healthcare systems. New medical devices can automatically monitor and control patient status and conditions without manual intervention, improving treatment processes, making healthcare systems more flexible and enabling better use of resources. However, this increase in communication capabilities and software reliability also implies greater security needs. As digitization in the sector has brought with it numerous benefits, it has also increased exposure to cyberattacks. Thus, in a very short time, the healthcare sector has become one of the most attractive targets for cybercriminals.
The healthcare sector is targeted by cyber-attacks mainly because it holds sensitive patient information, such as financial data, identification data and medical records. However, the consequences of these attacks can go beyond data theft and financial losses: an attack on these infrastructures could jeopardize healthcare operations. Hence, the potential consequences of these attacks are serious: operational disruptions, damage to the hospital's reputation, fines for breaches of regulations - such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union - or even worse, such as harm to patients. Such incidents have already caused serious consequences in some well-known cases:
- Düsseldorf University Hospital, September 2020. Systems failure caused by a cyber attack. Treatment of a seriously ill patient was delayed by one hour, which ultimately made it impossible to save his life.
- Cyberattack on the Irish health service (HSE Ireland), May 2021. One of the largest attacks against a healthcare IT system. This Ransomware attack caused a total shutdown of the IT systems. A high number of medical appointments had to be cancelled, being able to provide only minimum services.
- Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, March 2023. A Ransomware attack left this hospital paralyzed for more than a week, allowing only emergency operations and minimum services.
In this context, we analyze the current state of the cybersecurity landscape in the healthcare sector and the key measures to protect yourself.
To do so, we must understand that the hospital environment is characterized by the integration of various technologies. In addition to Information Technology (IT), it can be identified in three key components: healthcare networks, building management systems (BMS) and medical devices. These healthcare organizations contain an average of 20,000 devices, including communications in their medical networks of IT, IoMT, OT and IoT devices.
Increase in cyber-attacks in the healthcare sector.
The healthcare sector has experienced a notable increase in cyberattacks, presumably due to the lack of maturity in cybersecurity, and the high profitability obtained by attackers. Some figures from the report prepared by ENISA on cybersecurity in the healthcare sector in Europe provide more details on the current situation:
- It is estimated that 7% of all cybersecurity incidents affect organizations in the healthcare sector.
- For 12 consecutive years, the healthcare industry has had the highest average cost linked to security breaches.
To these figures it is necessary to add some notes on the current prevalence of ransomware, as it is one of the main cybersecurity threats in the healthcare sector.
In this regard, according to our report 'Ransomware Panorama 2024', Spain is the seventh most affected country in the world by this type of cyber threat (behind only the US, followed by Canada, the UK, Germany, France and Italy).

The report also highlights the ten sectors most affected by ransomware, with the healthcare sector in third place behind only manufacturing industries and customer services.
Why is the healthcare sector a key target for cybercriminals?
Simply put, the healthcare sector combines a number of factors that make it particularly attractive to cyberattackers:
- It presents high-value sensitive data, with personal, medical and financial information that can be used for a wide range of illicit purposes: from its monetization (through the payment of a ransom in the case of
- ransomware attacks), to its sale on the black market, or the execution of identity or insurance fraud, in addition to the request for fraudulent medication or treatment.
In this regard, according to the aforementioned ENISA report, threats linked to data breaches and ransomware are the most significant in the healthcare cybersecurity landscape.
Attackers seek to obtain large amounts of data in a single attack with which to maximize profit. Kaspersky data estimates that the price of a medical record on the dark web can be between $30 and $1,000 (while the value of a credit card is between $1 and $6).
- Healthcare organizations require continuous operation, where the priority falls on patient availability and safety. The disruption of healthcare services due to a cyber-attack has a critical impact: in addition to social alarm and reputational damage, it can put lives at risk. This is especially true for hospitals and, more specifically, for emergency services. This focus on availability in turn makes IT actions and maintenance more difficult, turning normally routine actions, such as the implementation of a security patch, into delicate activities that require a great deal of planning.
- The integration of various technologies with high interconnectivity and heterogeneity opens the door to a multitude of potential vulnerabilities and a high number of entry vectors. Old and obsolete systems coexist and communicate with new technologies, generating a complex and difficult-to-integrate digital environment, for which specific and robust cybersecurity measures are necessary.
- The lack of cybersecurity awareness, resources or knowledge in the sector can act as an incentive for cybercriminals, making the healthcare sector an easy target for attackers, where many of the basic security measures are not implemented. In this regard, the ENISA report reveals a worrying picture: only 27% of organizations have implemented a ransomware defense program; 40% have no cybersecurity awareness policies beyond the IT team; and 46% of organizations have never conducted a risk analysis.
Risks and consequences of cyberattacks.
The main risks faced by a healthcare infrastructure when suffering a cyberattack include the closure of emergency services, the need to resume paper patient registration, the cancellation of medical appointments and interventions and, as a consequence, the risk of endangering patients' lives. Some of these repercussions were seen in the incidents at the University Hospital in Düsseldorf (Germany) or at the Hospital Clínic in Barcelona, among others.
In addition to these risks directly affecting patient health, data breaches in the industry present a direct threat in the following areas:
- Exposure of personal information, such as identification data, medical records or financial data.
- Risk of fraud and identity theft. When cyber-attacks on healthcare infrastructures occur, patient phishing campaigns increase.
- Threats to patient privacy and security .
- Loss of trust and reputation for healthcare institutions.
- High financial impact. IBM figures put the average cost of this type of attack in the global healthcare sector at 10.93 million dollars, well above the 4.45 million estimated average cost for all sectors.
- Institutions face not only fines and sanctions from the authorities, but also non-compliance with data protection regulations such as the GDPR in Europe. On several occasions, there have been class action lawsuits from patients to the affected centers, denouncing the lack of protection of their data.
X-ray of cyber-attacks on the healthcare sector
The ENISA report cited above serves us to analyze some important data on cybersecurity in the healthcare sector today:
Main affected parties
The report reveals that healthcare providers account for 53% of the total number of incidents (with hospitals being particularly affected, accounting for 42% of this percentage); the report also highlights attacks on medical authorities and agencies (14%) and the pharmaceutical industry (9%).
Types of attacks
54% of healthcare cybersecurity attacks are ransomware attacks. Within these, 43% included data theft or data breaches and, in any case, 46% of incidents targeted access to healthcare data.
Likewise, the report puts the spotlight on the rise of Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks as another of the growing threats to cybersecurity in hospitals and other healthcare players.
Attack vectors
The report cites the following as the most frequent gateways in 2021:
- Incorrect security configurations (68%).
- Human error (16%)
- Malicious actions(16%).
These attack vectors are favored by the widespread presence of vulnerabilities, the use of unsupported operating systems and insecure device configuration. Additionally, it should be noted that these entry vectors do not only affect IT systems, but also medical devices, building management systems (BMS) and IoT technologies and their variants (IoMT and IioT), which are often implemented and maintained without the necessary cybersecurity measures.
Figures on the impact of cyber-attacks
Regarding the impact of cyber-attacks on the healthcare sector, the ENISA report compiles the following data:
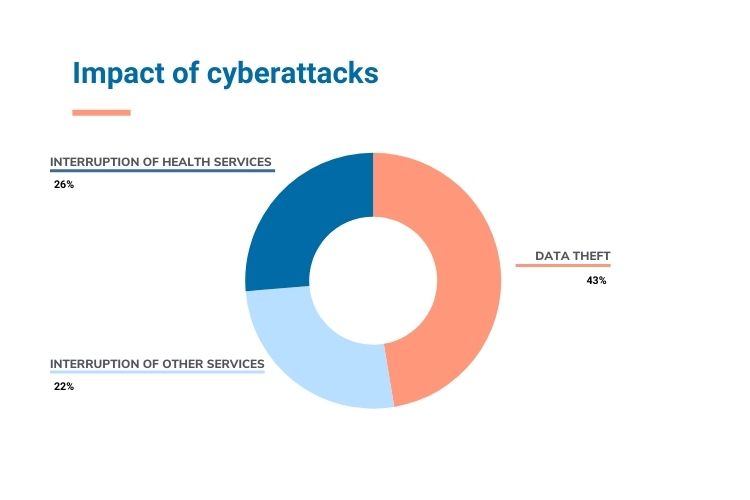
- 43% of the incidents achieved data theft.
- 22% caused the interruption of healthcare services and 26% caused the interruption of other services unrelated to healthcare services.
- Regarding the financial impact, ENISA's report draws on its 2022 NIS Investment study to value the average financial impact at €300,000 for cybersecurity incidents in the healthcare sector. To this figure must be added the reputational damage, which is difficult to quantify, that follows such an attack.
Key cybersecurity measures in the healthcare sector
Implementation of robust security policies and measures.
Development of a coherent and standardized framework of cybersecurity measures, including the following key points, among others:
- Encryption of data in transit and at rest.
- Multifactor authentication for accessing critical systems.
- Continuous monitoring of networks and systems through intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS).
- Incident and alert response system.
- Alignment with privacy regulations and standards. This often involves a constant updating process, taking into account the introduction of new regulations or the modification of those already approved.
- Implementation of rules and regulations, such as the National Security Scheme in Spain.
- Recurrent cybersecurity audits, taking into account the different technologies involved in the healthcare sector, with a view to detecting possible errors to be corrected proactively.
- Implementation of key technologies such as firewalls and review of implemented rules.
- Planning and development of backups.
- Establishment of efficient Access Control policies, based on the principle of least privilege and Identity and Access Management (IAM).
- Implementation of policies to implement security updates and patches, mitigating known vulnerabilities, whenever possible.
- Network segmentation and redundancy in the different dependent centers. In addition, generate isolated networks for the most critical devices that cannot be updated.
In addition to these measures, collaboration between the IT, OT, security and medical departments is essential when implementing new equipment. This is the only way to ensure that the adoption of new technologies and systems does not take place at the expense of cybersecurity in the organization. Thus, appropriate controls and countermeasures should be installed in any new technology adoption process.
Staff training and awareness
Ongoing training on secure information handling practices is essential not only for technical teams but also for physicians and administrative staff. This includes the importance of awareness of attacks such as phishing and other social engineering tactics, as well as good practices when sharing information or surfing the Internet.
In addition to recurrent training or courses, it may be useful to implement regular security incident drills, preparing staff to react to scenarios they may face.
In any case, the ultimate goal is the development of a true cybersecurity culture in which everyone involved in the organization knows what their role in healthcare cybersecurity is and how to maintain it.
In this area, it is especially important for senior management to be involved in this process, encouraging training and cybersecurity. From their position of influence, awareness of the importance of healthcare cybersecurity must reach all layers of the organization, including clinicians who work directly with devices and patient information.
Incident response planning
Developing a well-defined and regularly tested incident response plan can make all the difference in a context where the question is not so much “if” an incident will occur, but “when” it will occur. Thus, it is a matter of adopting a preventive approach in which action is taken in unison to minimize damage through robust containment measures.
Ensuring a quick and effective reaction to a data breach can fall back on the implementation of practices such as:
- Simulation exercises through tools such as Red Team and Blue Team.
- Development of an incident response team and an incident response plan.
- Development of Playbooks oriented to the health sector and the organization's dependent systems.
- Taking into account not only IT technologies, but also medical devices and OT systems when developing the different cybersecurity actions.
- Implementing a business continuity plan that, when applied to the healthcare sector, ensures that organizations can continue to offer critical services even in the event of a cybersecurity incident.
In short, this look at the different aspects of cybersecurity in the healthcare sector reveals that it is a multifaceted challenge that requires a fully comprehensive strategy. All with one goal: to protect the lives of patients, while keeping their information secure and safeguarding the availability of medical systems at all times.
There are many fronts and challenges to be addressed: from the complexity of protecting a wide variety of interconnected systems and devices, to the need for strict regulatory compliance.
In this context, having allies and cybersecurity experts on board is essential. This is where S2 Grupo comes into play. With two decades of experience in the cybersecurity sector and having become a benchmark company in Europe and Latin America, we are working to become the cybersecurity allies that the healthcare sector needs.
Therefore, we have developed a specific set of cybersecurity services for the healthcare sector. Aimed at a wide variety of stakeholders (public and private healthcare, mutual insurance companies, device manufacturers and government agencies), our portfolio includes key solutions such as:
- Healthcare SOC.
- Best practices and recommendations reports.
- Ethical hacking of healthcare equipment.
- Comprehensive cybersecurity assessments (IT and OT) specialized for healthcare environments, focused on IT systems, OT systems (BMS) and medical devices.
- Analysis of OT systems and medical devices, as well as the implemented network architecture.
- Specific awareness for the healthcare environment.
- Traffic monitoring probe for medical imaging modalities with DICOM analysis.
- Consulting for compliance with cybersecurity standards, such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
- HIPAA and GDPR compliance.
As part of our cybersecurity solutions, we use proprietary technology capable of responding in an agile and flexible manner to the specific challenges faced by the healthcare sector.
In addition, our vision of cybersecurity in the healthcare sector is a multidisciplinary approach: the healthcare vision, the business vision and the cybersecurity vision. For this reason, we have a team made up of biomedical engineers, industrial engineers and computer and telecommunications engineers.
Want to know more about how we work and our specific healthcare cybersecurity solutions? Contact us and let's talk about how we can help you protect your organization from cyber threats.
